A crucial element within the SAP ERP system, SAP Treasury and Risk Management (TRM) offers an array of instruments for the effective administration of financial transactions, risk factors, and treasury undertakings. This encompassing system covers a diverse set of operations including the management of cash and liquidity, investments and debts, as well as the handling of market and credit risks. Furthermore, it facilitates comprehensive financial reporting, through its extensive range of functionalities.
The primary objective of SAP TRM is to optimize an organization’s financial management operations, reduce costs, and mitigate financial risks. By leveraging real-time insights and visibility into financial positions and exposures, SAP TRM empowers organizations to make informed decisions about their financial transactions and risks, leading to enhanced cash management processes and streamlined treasury operations.
The purpose of Treasury and Risk Management is to:
- Capture deals and instruments for position management
- Manage risks and exposures.
- Execute accounting processes for settlement, valuations, month-end, etc. with full integration to GL.
- Perform analysis against deals and instruments including credit risk, market risk, and portfolio analysis.
- Integrate with Cash and Liquidity Management for liquidity visibility and investing/borrowing decision-making. `
- Integrate with IHC for intercompany netting and settlements on behalf.

The core Treasury process can be split into the following sections:
- Master Data(Business Partner, Security Account, Future Account, Security Class, House Bank
- Transaction Manager(Front, Middle, Back Office and Accounting)
- Market Data Import and Trade Platforms (Currency Rates, Security Prices, Yield Curves, and trade imports)
- MRA (Market Risk Analyser)
- CRA (Credit Risk Analyser)
- Payment Method and Procedure
- Cash Management and Liquidity Planning
- Exposure and Hedge Management
1. Master Data
Master Data pertains to the fundamental data entities crucial for the administration of financial transactions, cash management, and risk management procedures. These Master Data elements form the basis for all Treasury-related operations within the SAP system.
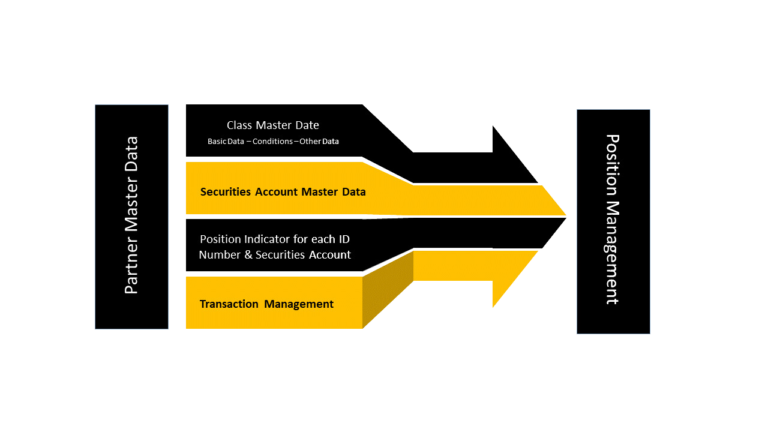
Master Data in SAP Treasury typically includes the following:
Business partner: The component Treasury and Risk Management uses as the business partner the SAP Business Partner for Financial Services. SAP Business Partner (BP) for Treasury is a segment of SAP’s treasury management software that facilitates the efficient management of financial interactions with banks, counterparties, and other financial institutions.
For each master data set, the business partner must be authorized. The following business partner roles are used for treasury functions:
- Counterparty → to identify the parties involved in trading
- Issuer → Issuer of the security class
- Depository Bank → safe keeper of the security position
Security Class: You must enter master data for each security managed in the position. Normally Bonds, Shares, and Mutual Funds are created as security classes. Class master data contains the product-specific conditions and all the general structure characteristics for securities.
Securities account: The securities accounts created in the system usually correspond to actual securities accounts at a bank. Security positions can be created in active, passive, or lending securities accounts. Securities accounts are used to manage positions and are required in all transactions that require position management.
House Bank: It is the bank with which a company maintains bank accounts. These banks can be used for various financial transactions, such as payment processing, cash management, and electronic bank statement processing.
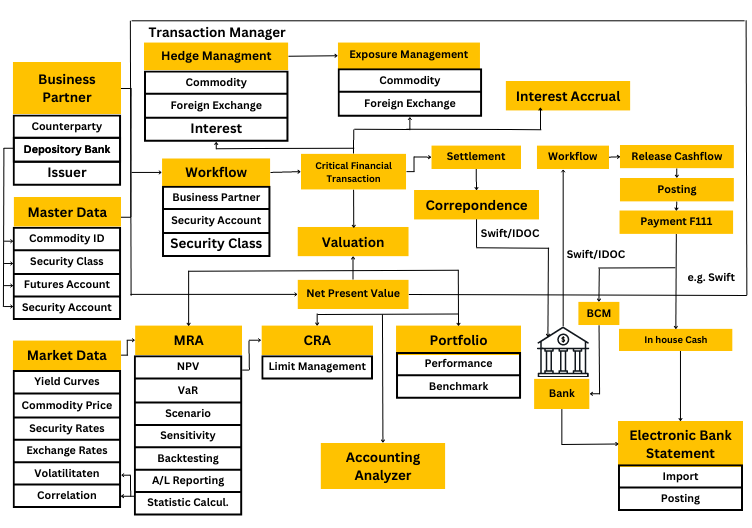
2. Transaction Manager
TRM provides a comprehensive solution for managing financial transactions, such as money market, foreign exchange, and derivatives transactions. The SAP TRM process typically involves below specified key steps:
Transaction entry: The first step is to enter the financial transaction details into SAP TRM. This involves specifying financial instruments, transaction type, parties involved, and the relevant terms and conditions.
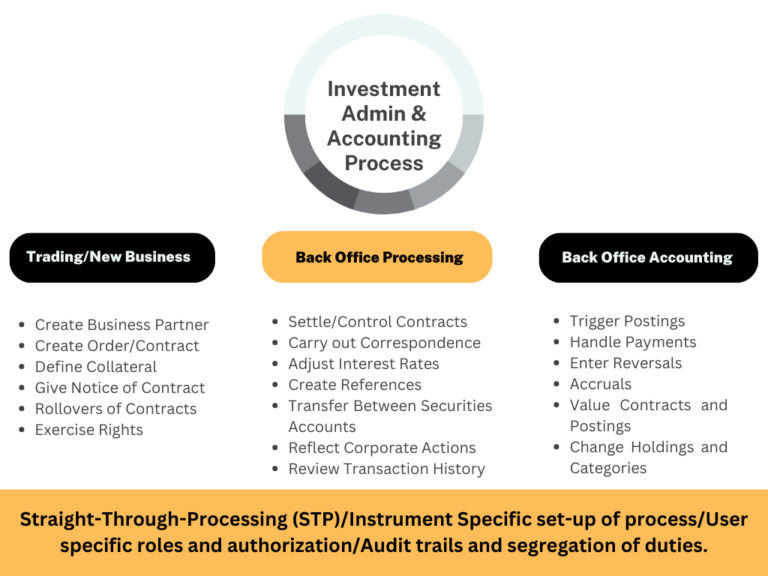
Transaction processing: After transaction creation, it is processed according to the specified terms and conditions. This may involve executing trades, settling transactions, and managing cash flows.
Accounting and reporting: SAP TRM provides tools for managing the accounting and reporting aspects of financial transactions. This includes generating accounting entries, preparing financial statements, and producing regulatory reports.
Integration with other modules: SAP TRM integrates with other SAP modules, such as Financial Accounting and Materials Management, enabling organizations to leverage their existing SAP infrastructure for financial transaction management.
3. Market Data Import and Trade Platforms
Market data import refers to the process of importing external market data into TRM systems or applications for risk analysis, valuation, and decision-making purposes. TRM systems rely on accurate and timely market data to assess and manage various financial risks, such as interest rate, foreign exchange, commodity price, and credit risk.
TRM systems rely on accurate and timely market data to assess and manage financial risks. Market data import involves bringing external data, such as instrument prices, interest rates, volatility surfaces, and economic indicators, into the TRM system for risk analysis, pricing, and decision-making. This data can be obtained through various sources, including market data vendors, financial data providers, or direct data feeds from exchanges. Market data import ensures that the TRM system has up-to-date information to accurately assess and manage risks.
Trade platforms facilitate the execution of financial trades and provide access to various financial markets and instruments. TRM systems integrate with trade platforms to capture trade data and automate trade workflows. By connecting to trade platforms, the TRM system can retrieve trade details, confirmations, and settlement instructions. This integration streamlines the trade capture process, ensuring accurate and timely data entry into the TRM system.
Trade platforms often provide real-time market data and price feeds to users. When integrated with TRM systems, these trade platforms can also provide market data directly to the TRM system. This integration allows the TRM system to access real-time or delayed market data from the trade platform, eliminating the need for separate market data feeds or sources. The TRM system can leverage this integrated market data to perform risk analysis, valuations, and decision-making.
TRM systems use trade platforms to execute trades and manage trade-related risks. The integration enables the TRM system to communicate trade instructions directly to the trade platform, facilitating trade execution. Additionally, the TRM system can receive trade confirmations and updates from the trade platform, ensuring accurate capture of trade data for risk analysis and reporting. This integration streamlines the trade lifecycle management process, allowing for efficient risk monitoring, position management, and compliance with regulatory requirements.
Overall, the integration of market data import and trade platforms in TRM enhances the accuracy and efficiency of risk analysis, trade execution, and trade management processes. It enables seamless communication of trade data between the TRM system and the trade platform, ensuring a comprehensive view of financial positions and risks.
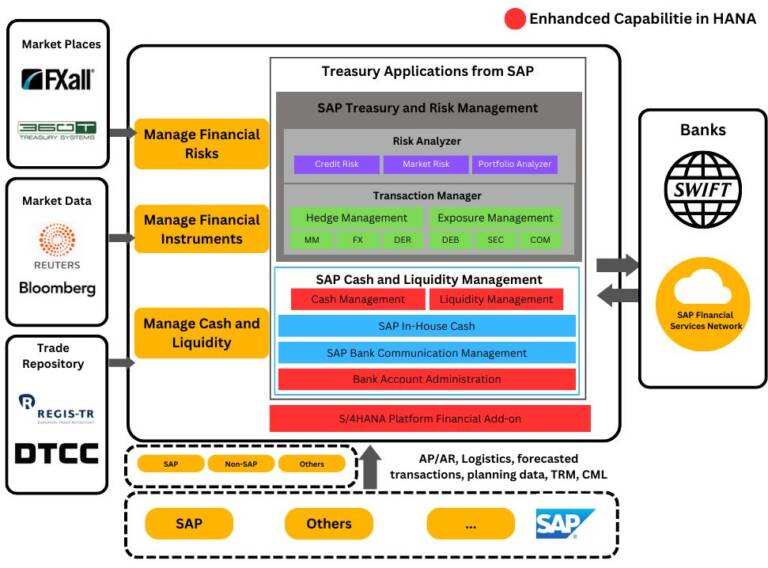
Market data consists of information such as exchange rates, interest rates, volatilities, and security prices. The market data is typically imported from an external source such as Bloomberg or Reuters. The SAP system supports a number of different options for importing market data. The volume of market data to be imported typically drives the method selected for uploading market data into the SAP system and would be an implementation-specific decision.
There are different options for implementing the retrieval in SAP.
Below are the different options for importing market data into SAP:
- Manual entry.
- File interface.
- Data feed
- Some market data, in particular statistical data (volatilities and correlations), can also be calculated directly in SAP.
- SAP is integrated with these systems to execute trades, verify correspondence, and trade request accuracy
4. MRA
SAP MRA proves especially advantageous for financial establishments engaged in intricate and unpredictable markets. This tool assists them in effectively monitoring shifting market dynamics, enabling well-informed judgments regarding their risk management tactics. The implementation of SAP MRA empowers these institutions to curtail their susceptibility to market uncertainties, enhance their risk management protocols, and bolster their overall fiscal resilience.
The Market Risk Analyser offers comprehensive position analysis functions, such as risk simulations, scenario analysis, and stress testing. Additionally, you can determine risk or performance key figures such as exposure, future value, effective interest rate, internal rate of return, sensitivity, and value at risk. When you run these reports, you can incorporate both contracted positions and fictitious financial transactions in the calculations. Valuations, based on the current net present value for each transaction and group via a user-defined portfolio hierarchy, can be calculated. All NPV’s are calculated in the MRA module and saved in the Transaction Manager to carry out the monthly and year-end valuation. For risk-controlling requirements, real or simulated market prices can be used. It also provides reporting capabilities that enable financial institutions to generate risk reports for internal and regulatory purposes. Different components are:
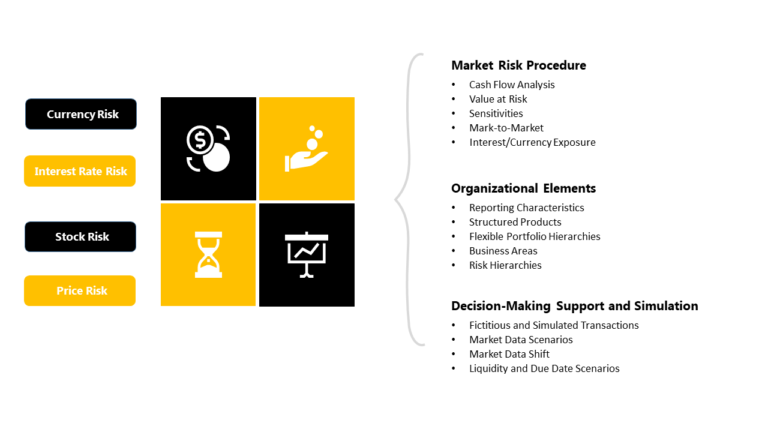
This component provides tools for collecting, validating, and processing market data from various sources, such as external market data providers, trading platforms, and internal systems.
This component performs complex risk calculations, such as Value-at-Risk (VaR), stress testing, and scenario analysis. The calculations are based on market data, portfolio holdings, and risk management policies.
This component aggregates risk exposures across multiple portfolios, business units, and geographies. It enables financial institutions to identify concentrations of risk and understand the impact of market events on their overall risk profile.
This component provides a range of reporting options, including standard and ad-hoc reports, dashboards, and alerts. It enables financial institutions to comply with regulatory reporting requirements and communicate risk information to internal and external stakeholders.
SAP MRA integrates with other SAP solutions, such as SAP S/4HANA and SAP Analytics Cloud, as well as with third-party systems. This enables financial institutions to leverage existing data sources and systems, and to streamline their risk management processes.
5. CRA
The tightening of regulations on risk control confirms the growing importance of analyzing and limiting the risk of insolvency. You also need system support for measuring, analyzing, controlling, and limiting counterparty/issuer default risk for business reasons.
SAP Credit Risk Analyzer is designed to meet all these requirements with the objective of providing you with comprehensive support for controlling counterparty/issuer default risks. This module provides a set of tools for analyzing and managing credit risk associated with financial transactions. It is designed to help organizations identify, quantify, and mitigate credit risk, and improve their credit risk management processes.
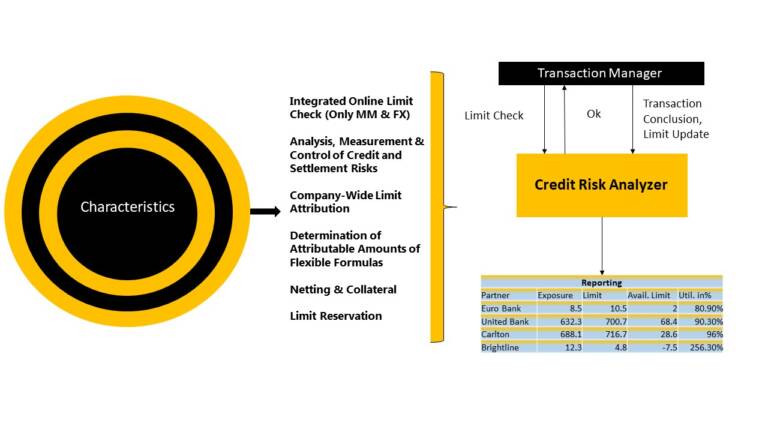
SAP Credit Risk Analyzer provides a range of features and functions, including:
Credit risk assessment: SAP Credit Risk Analyzer enables organizations to assess the creditworthiness of their counterparties and customers by analyzing financial statements, credit ratings, and other relevant data.
Credit limit management: This component provides tools for managing credit limits, including setting credit limits, monitoring credit utilization, and managing credit exposure.
Credit risk monitoring: SAP Credit Risk Analyzer provides real-time monitoring of credit risk, enabling organizations to identify and respond to changes in credit risk exposure.
Credit risk reporting: This component provides a range of credit risk reports, such as exposure reports, limit utilization reports, and credit rating reports. These reports enable organizations to gain insights into their credit risk exposure and make informed decisions about credit risk management.
Integration with other modules: SAP Credit Risk Analyzer integrates with other SAP modules, such as Sales and Distribution and Financial Accounting, enabling organizations to leverage their existing SAP infrastructure for credit risk management.
6. Payment Method and Procedure
Transaction F111 serves the purpose of initiating the Payment Program dedicated to managing Payment Requests. This feature offers an additional avenue for automated payments within the SAP system. Differing from the regular payment program, this process doesn’t rely on open items (like customer invoices) but instead centers around payment requests.
In scenarios where you need to create payment requests for specific dealings with a business partner, you have the option to define these requests within the permanent instructions linked to the payment details of that particular business partner. To accomplish this, you must activate the Payment Request indicator within the Standing Instructions of the payment details. It’s also necessary to input at least one payment method within the Payment Methods field list. These configured settings stand as the default parameters for the payment details for all transactions involving that particular business partner.
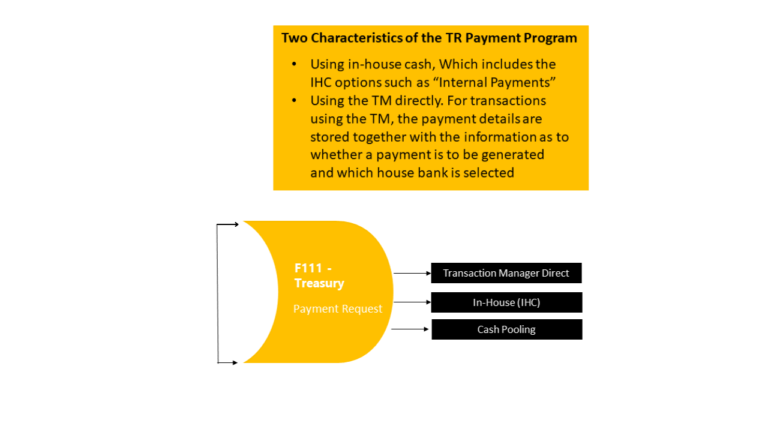
7. Cash Management and Liquidity Planning
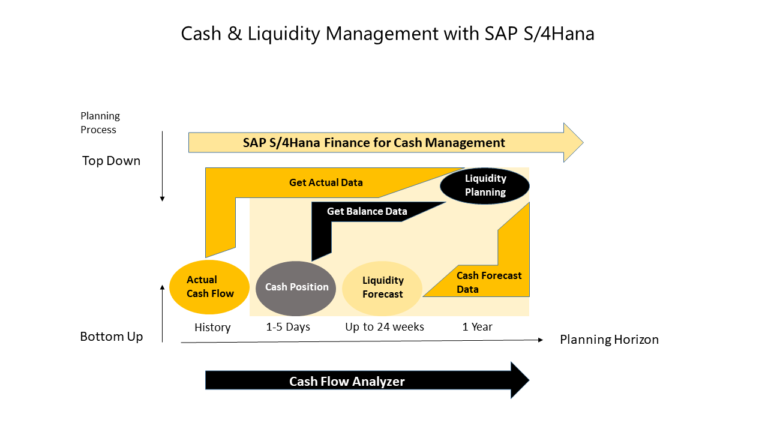
SAP Cash Management is a module of SAP ERP that helps organizations manage their cash flows effectively. It provides real-time visibility into cash positions, enables forecasting and liquidity planning, and supports cash transactions and bank communication.
The main features and functions of SAP Cash Management include:
his functionality enables organizations to track their cash positions in real-time by consolidating cash balances across multiple accounts and entities. It provides a comprehensive view of cash flows, enables drill-down to transaction-level details, and supports cash concentration and pooling.
SAP Cash Management allows organizations to forecast their cash flows and plan their liquidity needs. It supports short-term and long-term planning, enables scenario analysis and what-if simulations, and provides alerts for potential cash shortages.
The module supports cash transactions such as cash receipts, disbursements, transfers, and reconciliations. It provides workflows for approval and processing, supports integration with bank systems and payment gateways, and enables automated matching of cash flows.
SAP Cash Management facilitates communication with banks through various channels such as electronic banking, SWIFT messaging, and host-to-host communication. It provides a central repository for bank account information, supports bank statement processing and reconciliation, and enables secure transmission of payment files.
he module offers an array of analytics and reporting functionalities for the purpose of tracking and comprehending cash movements. It encompasses pre-built reports and dashboards for assessing cash position, forecasting liquidity, conducting bank account analysis, and performing cash flow scrutiny. Furthermore, users have the capability to fashion personalized reports and seamlessly incorporate them into external reporting tools.
In summary, SAP Cash Management helps organizations optimize their cash flows by providing real-time visibility, enabling liquidity planning, supporting cash transactions and bank communication, and providing analytics and reporting capabilities.
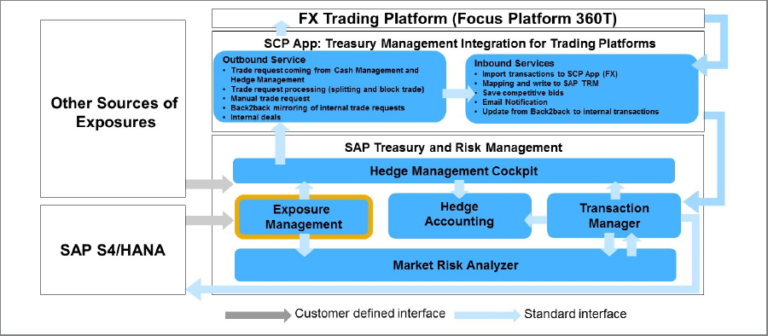
Exposure management refers to the process of identifying, assessing, and managing financial risks associated with foreign currency exchange rates and commodity prices. These Exposures are often held in various systems or even Excel. The Exposure Management delivers the possibility to upload, group, match, and store the raw exposures as well as the exposure positions which shall be used as hedge items in the Treasury system.
The exposure management function enables you to manage your foreign currency exposures and transfer them to hedge management. The integration with the SAP TRM module is illustrated in the next figure:
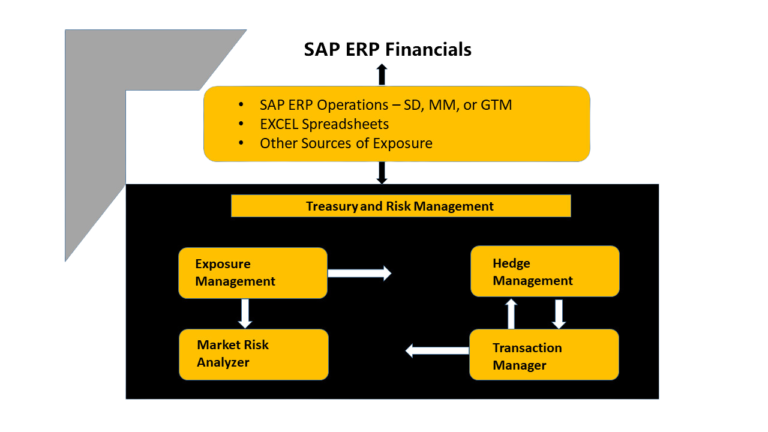
The process many companies follow is the middle office collects exposure data based on forecasted cash flows in risk currencies from various sources. They consolidate the exposure data to enter it into the SAP system as Raw Exposures. The exposure data should be aggregated in granularity, which differentiates
- Company code
- Risk currency
- The period when the exposure is due
Once the exposures are known and loaded into SAP, the hedging of the exposures starts, based on a company’s hedge policy.
Definition of Terms
- Exposure: In SAP Treasury and Risk Management, hedging activities are performed to hedge many different financial risks associated with your operating business. Different companies will have different financial risks based on their businesses however in an effort to use one standardized term for all risks, we use the term exposure to describe such a financial risk.
- Raw Exposure: In Exposure Management, only the basic data relating to your operative business transactions is stored in a raw format known in the system as raw exposure. A raw exposure is a basic mapping of an operative business transaction.
- Sub-raw Exposure: All information relating to financial risks is stored in sub-raw exposures. Sub-raw exposures form part of a raw exposure. A raw exposure can contain several sub-raw exposures.
- Exposure Position: The raw exposures taken together represent the financial risk associated with a company’s operation. The total risk position is known as an exposure position, which comprises several sub-raw exposures.
- Differentiation and Exposure Transactions: Differentiation enables you to define how risks are divided. The sub-raw exposures are initially converted into a temporary intermediate format. They then become exposure transactions and are used to create exposure positions.
- Exposure Position Flow: Exposure transactions are used to create exposure position flows, which, in turn, create the exposure position. An exposure position generally contains several exposure position flows.
- Exposure Position Value: The exposure position value is the total value of the exposure position flows for one exposure position on a particular key date.
Key features of Exposure Management are:
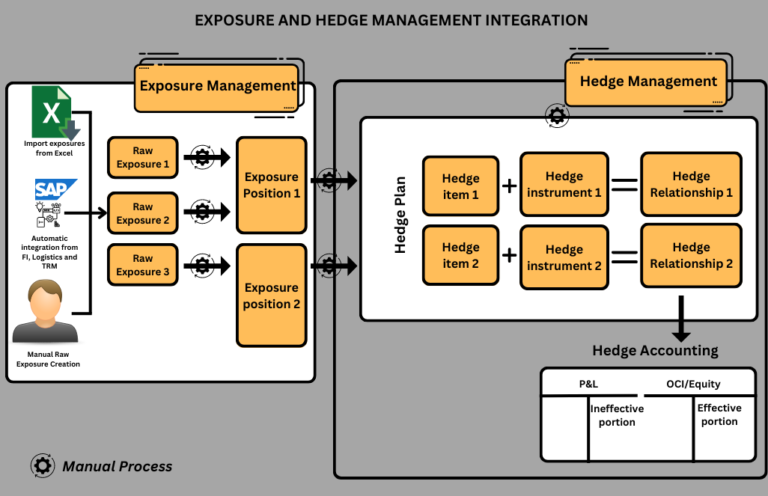
The system enables the identification and categorization of different types of financial risks, such as currency exposures resulting from foreign currency transactions or risks associated with fluctuation in commodity prices.
It helps to assess the potential impact of market fluctuations on financial positions by performing risk analysis and scenario simulations. This helps in understanding the magnitude of potential losses or gains.
Hedge Management provides comprehensive functions to manage financial risks related to currency, interest rates, and commodities. It provides a comprehensive platform for analyzing risks, creating hedging strategies, and monitoring hedge effectiveness.
The main features and functions of SAP Hedge Management include:
SAP provides a range of hedging instruments that can be used to mitigate financial risks as part of a Hedge Management solution. These instruments include options, forwards, futures, swaps, etc. These financial instruments can be configured based on client-specific requirements.
The solution offers the creation of hedging strategies to mitigate financial risks. It includes features for defining hedging relationships, selecting hedging instruments, and establishing target hedge ratios.
The solution provides functionality for testing the effectiveness of hedge relationships. Hedge effectiveness testing helps clients assess whether the hedging instruments effectively offset the changes in value or cash flows of the hedged items. If a hedge is considered effective, it qualifies for hedge accounting treatment; otherwise, it may be deemed ineffective, requiring adjustments or reconsideration.
Continuous evaluation and optimization of hedging strategies are important in TRM hedge management. This involves reviewing and adjusting hedging positions and strategies based on changes in market conditions, risk profiles, and corporate objectives.
The solution provides comprehensive reporting and analysis capabilities to monitor and evaluate hedge performance. Clients can generate reports and analyze data related to hedging activities, including hedge positions, hedge effectiveness, valuation, and other relevant metrics.
SAP Hedge Management streamlines and automates the management of hedging transactions, ensuring compliance with accounting standards and optimizing risk management processes. It provides a centralized platform to define, execute, and monitor hedge relationships, improving the organization’s risk management capabilities.
Effective hedge management in TRM helps organizations reduce exposure to financial risks, enhance financial stability, and support strategic decision-making. It requires a combination of risk analysis, hedging expertise, proper documentation, and robust monitoring and reporting capabilities provided by TRM systems.
Noshtek, as an SAP consulting company, plays a crucial role in helping organizations effectively implement and utilize SAP Treasury and Risk Management (TRM) solutions. With our expertise and experience, we support businesses in optimizing their financial management operations, reducing costs, and mitigating financial risks through the comprehensive functionalities offered by SAP TRM.
Here’s how Noshtek assists in SAP Treasury and Risk Management:
Noshtek offers expert consultation services to guide organizations in understanding their unique financial needs and challenges. They work closely with clients to tailor SAP TRM solutions to their specific requirements, ensuring that the implementation aligns with the organization’s objectives.
Noshtek assists organizations in the complete implementation of SAP TRM modules. This includes configuring the system based on the organization’s financial processes, setting up master data entities like business partners, security classes, securities accounts, and house banks, and establishing transaction processing workflows.
SAP TRM can be customized to cater to the intricacies of each organization’s financial operations. Noshtek helps tailor the system to accommodate specific transaction types, risk management strategies, reporting needs, and integration requirements.
SAP TRM modules need to seamlessly integrate with other SAP modules and external systems. Noshtek ensures smooth integration with modules like Financial Accounting, Materials Management, and Cash Management, as well as third-party data sources and trading platforms.
To assist enterprises in using the SAP TRM functions efficiently, Noshtek offers training programs. We provide continuing assistance to deal with any problems that develop after implementation and to make sure the system is updated and in line with shifting business requirements.
Noshtek provides firms with guidance on treasury and risk management best practices by drawing on our understanding of the sector. Informed judgments concerning financial transactions, risk mitigation techniques, and compliance standards can be made by enterprises thanks to this.
Noshtek assists organizations in identifying potential financial risks by analyzing their exposure to market fluctuations, interest rate changes, and currency fluctuations. This helps in devising effective hedging strategies and risk management plans.
With expertise in hedge management, Noshtek helps organizations create, execute, and monitor hedge strategies effectively. They guide clients in selecting appropriate hedging instruments, optimizing hedge ratios, and conducting regular effectiveness testing to ensure compliance with accounting standards.
Noshtek supports organizations in generating comprehensive reports and analytics related to their financial positions, risk exposure, and hedge performance. This enables informed decision-making and regulatory compliance.
In essence, Noshtek partners with organizations to navigate the complexities of SAP TRM, enabling them to streamline their treasury and risk management processes, enhance cash management, reduce financial risks, and make strategic financial decisions based on accurate and real-time insights. Our expertise ensures that organizations derive maximum value from SAP TRM solutions, contributing to improved financial stability and operational efficiency.

Looking for expertise and excellent know-how in matters of Corporate Treasury and Financial Asset Management?
Rahul Mittal
Managing Partner -Treasury & FAM
Around 12 years of experience in the information technology and 10 years experience in SAP. Extensive experience and knowledge of Insurance industry.Skilled in SAP TRM/FAM, IFRS9, SAP Profitability and Performance Management, S/4 HANA and Project Management. Strong professional with a Master’s degree focused in Finance from IBS Gurgaon backed with B-Tech in Information technology.

